Career
Due to the close cooperation with our customers from industry and research, new and advanced tasks and requirements are constantly arising.
The highly dynamic development process in the vehicle environment places above-average expectations on the performance and flexibility of our employees.
If you are interested in working in one of our development teams, have the above-mentioned qualities and have a degree in engineering with sound knowledge of FEM, then send us your complete application documents.
We have already given many students the opportunity to apply their knowledge of FEM to highly interesting topics in the form of a Diploma- , Bachelor- or master thesis to deepen.
We take the word "supervision" very seriously and thus enable the student to gain a deeper insight into the work of a refractive engineer.
The highly dynamic development process in the vehicle environment places above-average expectations on the performance and flexibility of our employees.
If you are interested in working in one of our development teams, have the above-mentioned qualities and have a degree in engineering with sound knowledge of FEM, then send us your complete application documents.
We have already given many students the opportunity to apply their knowledge of FEM to highly interesting topics in the form of a Diploma- , Bachelor- or master thesis to deepen.
We take the word "supervision" very seriously and thus enable the student to gain a deeper insight into the work of a refractive engineer.
If you are interested, please contact us and decide on one of our suggested topics.
job offer
As a partner to industry and research, we offer engineering services in the field of technical calculation/simulation (FEM) and component testing. We see our strength in the close connection between CAE and testing. We are looking for motivated, creative and team-oriented employees.
You can expect a diverse, interesting and, despite the rather theoretical reputation, a practice-oriented area of responsibility in which you can use your knowledge and expand it in a targeted manner.
Qualifications:
Please send your complete application documents to: info@makross.de
In addition, an inexpensive apartment is offered for a few weeks at the beginning of the probationary period!
You can expect a diverse, interesting and, despite the rather theoretical reputation, a practice-oriented area of responsibility in which you can use your knowledge and expand it in a targeted manner.
Qualifications:
- Graduate engineer f/m (FH/TU), Master/Bachelor f/m
- Work experience or graduate
- Knowledge in the field of FEM structural analysis
- Independent way of working and creativity
Please send your complete application documents to: info@makross.de
In addition, an inexpensive apartment is offered for a few weeks at the beginning of the probationary period!
1D-Shaker
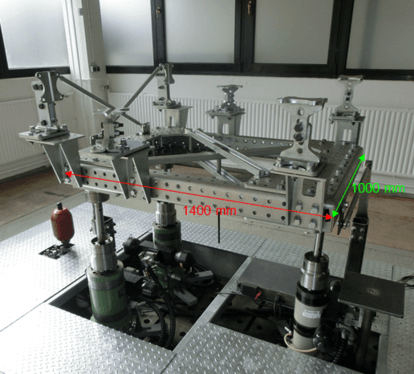
3D-Shaker / 4D-Schwingtisch
- 3 cylinders with 15 kN (each 1 Moog 761 63 l servo valve
- 3 flexible oscillating tables for different tasks
- Seismic mass 15 t
- Air suspension with additional volume (1.2 Hz natural frequency)